Breeding rabbits is a great way to provide the family with tasty and nutritious dietary meat, as well as make money on the delivery of furs to furrier enterprises. Rabbits are also bred for sale, but such a business is risky and will require knowledge, experience, time and financial costs from a rabbit breeder.
Therefore, if you are just starting out or are going to start the rabbits, then detailed instructions for caring for rabbits will help grow large and healthy fluffy pets, avoid common mistakes and frustration.
Table of contents
How to distinguish a rabbit from a rabbit?
Let's start with the question of how to distinguish a hare from a rabbit. The domestic rabbit is a subspecies of its European wild brother, adapted for living alongside a person. Separately allocated dwarf rabbit, whose weight does not exceed 1 kg. Breeding dwarf rabbit is carried out exclusively for decorative purposes.
The closest relative of the rabbit is the hare.
So, the difference between a hare and a rabbit is possible according to the following visual features:
- To size. The weight of mature rabbits reaches 11 kg (the common European hare rarely weighs more than 7 kg);
- According to the length of the ears. Rabbit ears are shorter (up to 10 cm) and wider than that of a hare (7-15 cm);
- By color. The color range of rabbits differs in its variety (shades of brown, gray, dark yellow colors prevail), and the color as a whole tends to homogeneity even in the presence of spots.The color of the hare is not catchy, often spotted, whose task is to disguise the color of the terrain;
- The muzzle of the rabbit is wider and larger than that of the hare. comparable sizes.

How to care for rabbits at home?
The rabbit is distinguished from other pets by the exceptional need for proper and careful care, which often prevents its mass breeding.
Rabbit care includes:
- Rational placement: one rabbit needs from 0.5 to 1 m2 free space;
- Separate content of females and males, young animals up to 3 months and adult animals. Pets with the smallest signs of disease should be immediately isolated from healthy animals;
- Maintain cleanlinessthat involves daily cleaning of the cages, changing the litter as it gets dirty, disinfection of the cages and equipment at least 2-3 times a month and when animals are moving.For disinfection, boiling water or a 1% formalin solution is used;
- Ensuring full and varied nutritionby water;
- Cell ventilation and walking in the warm season. In the presence of rabbit walking, it is advisable to carry out year-round;
- Daily inspection of rabbits, disease prevention and vaccination.
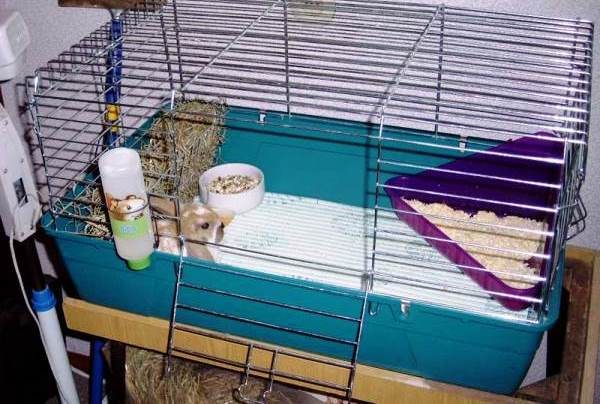
How to choose and equip a cage for the maintenance and care of rabbits in the apartment?
Experienced breeders make cages on their own, for which they need:
- Metal grid;
- Plywood sheets;
- Wooden boards and slats.
There are no standards for cell size, However, a parallelepiped-shaped cage with approximate parameters 40 × 70 × 60 cm is considered optimal, which makes up enough space for a pair of rabbits, making it easy to clean and disinfect the cage.
The walls and cage floor are made of metal mesh or wooden slats. When using the rails between them there should be gaps in the range of 1-1.5 cm for easy cleaning and ventilation. The rabbit door is made of mesh and must face the sunny side.
The cage requires the presence of litter.For arrangement use any available materials:
- Sawdust;
- Straw or hay;
- Needle branches, etc.
If the arrangement of several cells is planned, then it is best to equip a rabbit. It is a closed building, where cells are placed in several tiers. The log well warmed rabbit is necessary for districts where the temperature in the winter falls below -10 degrees.

The roof and outer walls of the rabbit's extreme cells are made deaf, preventing the ingress of air and moisture. If necessary, the walls can be further insulated with straw and other available materials. The rabbit's roof is insulated, covered with roofing iron or slate. This allows you to protect rabbits from moisture, drafts, and in winter from severe frosts.
It is worth thinking about the rational placement of rabbitry on the site. It is best to turn its face to the south-east. This will create a warm and comfortable environment for animals and protect them from direct sunlight. The space next to the rabbit's facade is enclosed and a place for free-range rabbits is created.
Feeding trough and drinking bowl
In a cage for rabbits there should be a feeding trough and a drinking bowl. For the manufacture of used household items. The main thing is that they should be firmly fixed and not allowed to climb in them with their paws. Feeding trough and drinker are simple and semi-automatic. Semi-automatic drinking bowl is arranged as follows:
- You will need two flat cans of canned food of different diameters, as well as a plastic bottle with a capacity of 1-1.5 liters;
- The smaller can is fixed inside the center of the larger can, limiting the rabbit's ability to spill water or climb into the trough with its paws;
- The bottleneck is placed in a larger jar, and the bottle itself bends so that, as the water from the jar disappears, it fills itself.
Semi-automatic feeder for dry bulk feed can be made similarly.
For a rabbit breeder who plans breeding pets, it will be necessary to equip a special device in the cage that imitates a hole - the mother liquor. Since rabbits live and breed in burrows in their habitats, they also need a similar construction in captivity., which you can do yourself.
For this, a wooden box with approximate parameters 30 × 40 × 40, made of boards or plywood, is used. In one of the walls of the box, you need a round hole with a diameter of 15 cm. And the lid of the box should open freely. At the bottom of the mother liquor is a bed of shavings or sawdust.
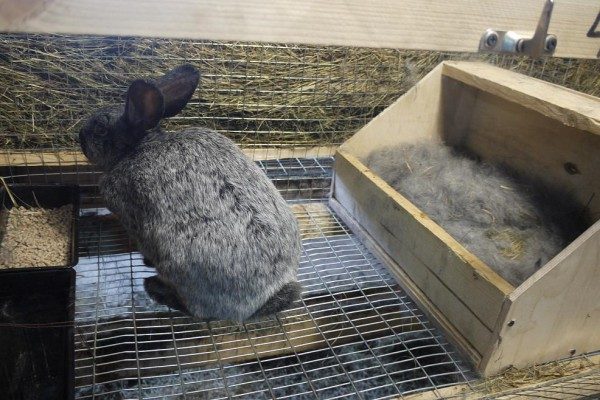

A little rabbit preparing for motherhood is placed in a cell with a mother liquorwhere the rabbits spend the first month of their lives. There is no need to equip the drinking bowl and the feeder in the mother liquor, but it is imperative to maintain cleanliness and carry out regular cleaning.
Feeding pets
Feeding rabbits in the conditions of an apartment will not cause trouble to the beginning rabbit breeder, the main thing to remember isthat rabbits are almost omnivorous and eat a lot. The exact calculation of the need for feed is determined empirically and depends on the weight of the animal. If it is necessary to stock up for a year, 1 adult rabbit will need 300-500 kg of products, 2/3 of which are grass or hay.
The summer diet of rabbits differs from the winter feeding in terms of caloric content, composition of feed, and presence of vitamins.
In the summer period for rabbits are suitable:
- Herbs, especially dandelion, clover, coltsfoot, alfalfa, colza, plantain, nettle. Herbs give dry, and even better slightly dried to improve digestion;
- The leaves of grapes, strawberries, raspberries, currants, lettuce and other shrubs and trees growing in the garden;
- Root vegetables (potatoes, beets, celery, carrots, Jerusalem artichoke, etc.). Tubers must be clean, without land, both raw and boiled;
- Some fruits and vegetables (apples, pears, cabbage, zucchini, etc.);
- Dry feed: grain and legumes, mixed fodder.
In winter, herbs are replaced by hay, straw, silage. Winter ration should contain more dry and nutritious feed than in summer. As a variety for rabbits, food leftovers from the table (except meat dishes and bones) are suitable.
To provide vitamins in winter, rabbits need needles.Spruce and pine branches are the best way to add vitamin C to the diet.
In the year-round ration is required to add chalk, at the rate of 1-2 g, salt 0.5-1 g per day.
Nutrition of young stock requires additional attention with regard to the still weak digestion. Therefore, only tender herbs and roots are suitable for young rabbits. Pumpkins and zucchini, Jerusalem artichoke, boiled potatoes are especially useful for baby rabbits. But from giving solid feed (hay, straw, grain) should refrain.
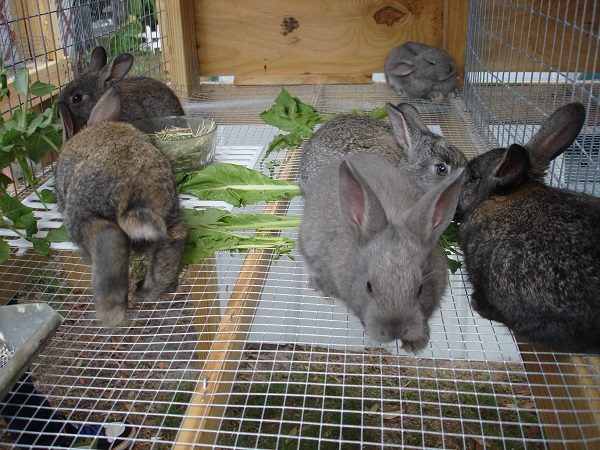

The diet of pregnant and lactating rabbits needs to be increased and increased due to nutritious foods: cereals, legumes, bran, mixed feed, root crops.
From the diet of herbs should be excluded:
- Elderberry;
- Ledum;
- Wolf berries;
- Dope;
- Celandine;
- Digitalis;
- Belena,
- Hemlock and a number of other poisonous herbs.
Diseases and their prevention
As in humans, rabbit diseases are usually divided into viral and non-viral. Most often, rabbits are susceptible to digestive disorders and respiratory diseases.
Colds, inflammations of the respiratory mucosa - the result of the action of cold, damp, drafts, crowding. It is possible to diagnose such diseases in the presence of sneezing, nasal discharge, redness of the oral mucosa, and general weakness.
Digestive disorders are caused by improper feeding of animals. Signs of such diseases: discharge, covered with mucus, containing blood, diarrhea, etc.
The best way to prevent the development of these diseases is to properly feed, care, protect animals from the harmful effects of the weather.
Veterinary medicine is also known for more than 30 viral diseases to which rabbits are prone. Among the most dangerous are:
- Salmonellosisresulting in viral bowel disease. Symptoms: fever, vomiting, weakness, diarrhea. The meat of diseased rabbits is forbidden to be eaten, and the carcasses of rabbits are cremated;
- Spirochetosisaffecting the genitals of rabbits. Symptoms: swelling, redness, bleeding, ulcers on the genitals;
- Colibacteriosis - intestinal infection affecting rabbits in violation of the rules of keeping and communicating with sick animals. The main symptom is diarrhea;
Myxomatosis spreads extremely quickly and as widely as possible, the incubation period of the disease does not exceed 2 weeks. Almost all diseased animals die. Symptoms of myxomatosis - the presence of tumors near the head and genitals.
Sources of infection can be ticks, mosquitoes, fleas. Also, the virus is transmitted from a sick animal to a healthy airborne route. The diseased animal must be immediately isolated. Also isolated animals that could contact with a sick individual. For a person, myxomatosis is not a threat.
Symptoms of necrotic hepatitis are almost impossible to notice due to the lightning spread of the infection. The disease occurs within 1-3 days. The main causes of infection - the interaction with sick animals. Necrotizing hepatitis causes enormous damage to the household, as all sick rabbits die.
As a prophylaxis of viral diseases, separate keeping of animals is used, and newly acquired rabbits are placed in a separate quarantine room, which can last up to 3 months.
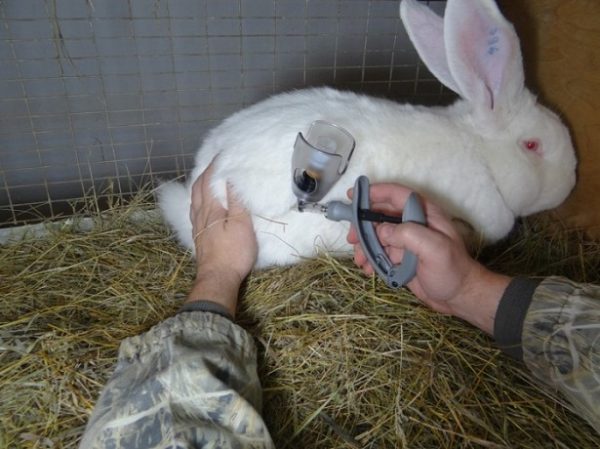
Vaccination
The fight against myxomatosis and necrotizing hepatitis is carried out with the help of an inexpensive and effective procedure - vaccination. Only healthy animals need to be vaccinated, starting at 45 days of age. In practice, both separate vaccines for UHD and myxomatosis are known, as well as the combined variant.
Keeping and caring for eared pets involves a lot of subtleties that are difficult to reflect in the article. Therefore, if you seriously think about the business of selling young animals, meat or skins, then you should pay attention to the specialized literature, the authors of which will give exhaustive answers to your questions. We wish you success in such a difficult task as rabbit breeding!
And finally, we suggest watching a small video on how to care for and keep rabbits:
