Today, there are many varieties of pears, but only some of them exist for more than a hundred years, and, in spite of that, at such a very respectable age, they are very popular and actively cultivated. One of these varieties is Williams pear.
We will talk about the description of this variety in this article.
Table of contents
History and Origin of Williams Pear
The Williams pear variety was obtained in southern England (Bekshire) in about 1796 by Wheeler. It was created based on the species of common pear, but which plants were definitely used as parents is unknown, therefore the origin of the Williams pear is considered uncertain.
Interestingly, it was named after Robert Williams, who first showed him to the organization for the cultivation of various fruit and horticultural crops (London) in 1816 and spent a lot of effort to popularize it. The next country where this pear variety was intensively cultivated was France (1828). A little later, he appeared in other European countries.
In the orchards of southern Russia, Williams appeared around 1860 from a private Crimean nursery.owned by the gardener N.P. Makuhinu. This variety is called differently: Barlet, Duchesse summer, Williams summer, red and Williams Bon-Chretien.

Growing region of summer varieties
In 1947, the hybrid underwent state variety trials,and was recognized as suitable for growing (zoned) for the North Caucasus region (North Ossetia, Karachay-Cherkessia, Krasnodar Territory, Kabardino-Balkaria, Adygea, Stavropol Territory, Chechnya and Ingushetia).
It is also actively cultivated in the Rostov region. and in many former republics of the Soviet Union (Moldova, Georgia, Ukraine, Tajikistan, Kirghizia, and so on).
Description and characteristics
Red pear is a reference among pears that ripen at the end of summer. It can be grown in large gardens of agricultural enterprises, in the garden and in the country. The pear is included into group of the best dessert grades of a world level which ripen in the late summer (August).
The crown of a tree has the shape of a wide or rounded pyramid and is often asymmetric. Young specimens grow fairly quickly, but when the trees reach the age of 10-12 years, the growth rate is significantly reduced. Also one of the reasons for the slowdown in the Williams variety is the high yields and the early onset of fruiting. Annual growth rates can vary from medium to weak.
Straight or slightly deviated thick branches covered with light yellowish bark witha small amount of lentils. The main skeletal branches and trunk are painted gray.
Rather large leaves shaped like an egg have a smooth and shiny surface. Along the raised edges of the leaf blade are fine teeth. Light green streaks protrude slightly above the surface.

Whitish cream flowers are collected in inflorescences of 6-7 pieces. They begin to bloom before the leaves appear. Abundant bloom lasts a long time.
Fruits in inflorescences are mainly tied in 2 or 3 pieces and firmly hold on the branches. The weight of a pear is 170 grams, but in young copies it can reach 180 grams.
Large or medium-sized fruits with a slightly bumpy surface covered with a thinish fragrant skin, painted in a light greenish color (during removable maturity). When fully ripe, it becomes a beautiful yellowish shade with gray specks. Sometimes on the side facing the sun, there is a tender pinkish stain. Fruits are attached to shoots with slightly curved thick stalks. The dark brown, rather small seeds have an ovoid shape and a sharp tip.
Juicy and tender flesh with an attractive dessert taste, nutmeg aroma and a slight sourness, painted in yellow-white color.
Variety Williams can be used in fresh form, for the preparation of compotes, jams, pickles, as well as for drying (universal).
The time of removable maturity comes in the second half of August. Fruits shot at this time are stored for about two weeks. Pears of this variety can be stored in the vegetable compartment of the fridge for about one and a half months.
Williams summer, vaccinated on a pear, begins to bear fruit at the age of 5-6 years, if he is grafted on a quince, then the first crop can be harvested already for 3-4 year. But it is worth remembering that such trees do not live long.
Productivity directly depends on growing conditions. For example, the average yield of a tree at the age of 12 to 18 in the Krasnodar Territory is 100-200 centners per hectare, and in the Crimea - from 80 to 150 kg per tree.
This variety belongs to the samobzheplodny and to obtain abundant crops need to be planted next to the variety pollinators. The best pollinators for Williams pears are Aleksandrovka, Pet Clappa, Bere Bosc, Olivier de Serres.

Advantages and disadvantages of red pear
This hybrid attracts attention:
- early fruiting;
- constant high yield;
- large beautiful fruits;
- undemanding to soil conditions.
The disadvantages include:
- poor winter hardiness;
- self-infertility and low drought tolerance;
- strongly affected by scab, sucker and aphids.
You may also be interested in the following varieties of pears:
Rules for choosing seedlings
For planting is best to choose 1-2 summer seedlings in height from 1.3 to 1.5 meters. In trees of this age, the distance from the root collar to the lateral shoots is more than 50 cm, and the number of branches varies from 3 to 5 pieces.
The length of the roots of seedlings of this age is 20-30 cm. Also on the young pear should not be mechanical damage., root growth and leaves (green or dried). The central shoot must also be well formed.

Landing
For the cultivation of pear Williams pick up a sunny plot with a nutrient permeable soil.
The best time for planting is autumn (when vegetation ends), but you can do it in the spring (before bud break).
A pit for planting is dug 60 to 60 by 80 cm in size. For backfilling the roots, it is advisable to prepare an earth mixture consisting of humus (one part), garden soil (one part), superphosphate (350 gr.), And potassium sulfate (350 gr.).
Before planting, the root system of the pear is inspected, cut off the broken and dried, and then soaked in a heteroauxin solution. (or any other root formation stimulator) for 3-12 hours.
In the planting pit, the roots are distributed evenly, first fall asleep with garden soil, and then with the mixture. This is done so that the roots do not come into contact with the mixture with fertilizers. At the same time be sure to ensure that the space between them was filled. After planting, the seedling is well watered, the soil is compacted a little and the ground soil is filled up.
Care
All tree care consists of watering, fertilizing, pruning, pest and disease control.

Watering
Young pears in the first 2-3 years after planting need regular watering throughout the season. It is desirable to cover the ground around the trunks with a layer of mulching material (peat, buckwheat husks or pine nuts, wood chips) with a height of 5 to 8 cm. This retains moisture in the ground, does not allow a large number of weeds to grow and reduces the amount of watering. In addition, mulching prevents the formation of a dense crust on the surface of the soil.
Mature trees water from 3 to 7 times per season, depending on climatic conditions and weather. But watering must be carried out before the blooming of flowers, after flowering and autumn, when the season ends.
Feedings
Young trees, before they begin to bear fruit, you need to feed each year in spring. To do this, the ground around the trees is mulched with rotted manure in a layer from 4 to 6 cm. It is also advisable to add 100-150 grams (per tree) of Kemira or azofoska.
Feeding adult pears is best done in the fallwhen digging is done.To do this, use mullein or other types of organic fertilizers in combination with mineral fertilizers (superphosphate and potassium sulfate). Fertilizers are scattered around the circle of pristvolny circle, which corresponds to the diameter of the crown and must be dug up to a depth of 25 to 35 cm so that the nutrients reach the root system.
If the crop is not expected to be very large, then you can make additional feeding before shedding the ovary.
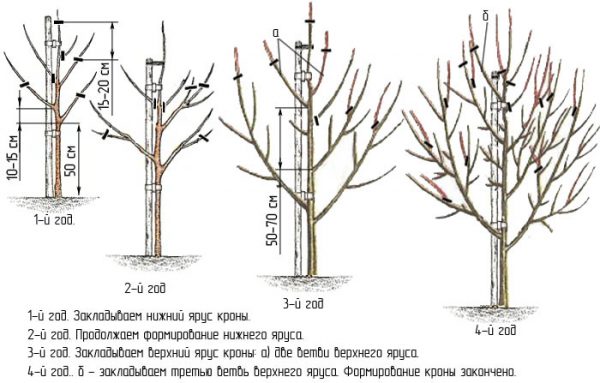
Pruning
Pruning young pears after planting is desirable to carry out in early spring. From 3 to 5 lateral branches are left on the tree, which should be located at a height of 50 to 70 cm above the ground. The central trunk is cut so that it is 15-30 cm higher than the highest lateral shoot. The length of the lateral shoots is necessarily reduced to 30 cm.
Pruning of adult trees is carried out twice a year. Sanitary pruning is carried out in order to regularly remove diseased, broken and dried branches. A rejuvenating pruning is also carried out, with the help of which the intensive growth of the plant is maintained and restored, as well as the number of points of fruiting is regulated.
During rejuvenating pruning, perennial shoots are shortened to 3-5 year old and older branches.If the growth of annual shoots has decreased to 15-20 cm, then a weak pruning is carried out (for 2-3-year-old branches), and if the growth is even smaller, then the pruning is enhanced. Even for thinning cut out part of the old fertile branches inside the crown.
Diseases and pests
Among the diseases with which this type of pear can be affected are the following diseases: cytosporosis, fruit rot, scab, rust and root cancer.
Cytosporosis occurs on the bark of the trunk and skeletal branches in the form of a slightly indented spot, painted in a brown-reddish tint. Cracks appear over the edge of the stain over time, and the bark tissues soften.
At the beginning of the disease, the diseased areas are cleaned and treated with copper sulphate, and then with garden pitch.
Rust appears on the upper surface of the leaves as orange spots rounded. In July, on the lower part of diseased leaves growths are formed in the form of blisters, where rust spores are formed.
To combat this disease, spray the following drugs: Bordeaux liquid (4% solution), colloidal sulfur (2% solution). Treatments are carried out before flowering, after it ends and after two weeks.
Scab first appears on the leaves in the form of green-black spots that grow rapidly. Then the leaves dry prematurely and fall off. In addition, scab infects the fruit and young shoots. Fruits form dense leathery spots, and the flesh beneath them cracks. The bark of diseased shoots is covered with cracks, they warp and dry.
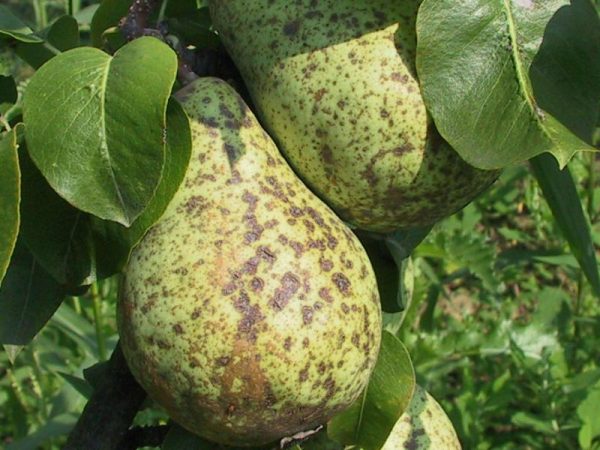

Prevention of this disease is the regular cleaning and destruction of diseased fruits and fallen leaves.
When scabs appear, trees are sprayed three times (before and after flowering, and two weeks later). For this use Bordeaux liquid and colloidal sulfur.
Methods of struggle
Among the pests that attack the pear, it is worth noting aphid, pear leaflet (caramel), pear gall mite, pear bug, California shield, green apple aphid.
Green apple aphid larvae feed on juices of young leaves from buds, and later on young shoots. Damaged leaves curl, dry and fall off. Young shoots stop growing and dry out.
Pear leaf leaf larvae, which feed on the cell sap of leaves, buds, buds and young shoots, cause great harm to pears. As a result, the leafblock causes a massive fall of leaves, ovaries and flowers, as well as underdevelopment of fruits and twisting of shoots.
When this pest occurs, several sprays are carried out (during the swelling of the kidneys, in the summer and autumn). To do this, use tools such as Iskra, Inta-Vir, Aktara and Commander.
Gardeners reviews
Oksana, Zaporozhye: In our 6th year two trees of this variety grow. Low, sprawling trees. Yields are amazing. All branches are simply covered with fruits, for each branch they made props, otherwise they would not have survived. Such an abundance of fruits causes delight not only among us, but also among neighbors and everyone who comes to visit. Very tasty pear, juicy, sweet. Very pleased.
Makar, Crimea: Williams summer in the Crimea is also called Dunka, very sweet and cool, and fragrant. And unlike Klapp Favorite, it does not spoil quickly, in the middle. Here Klapp really becomes "mushy" when overriding, and brown in the middle. So it is necessary to consume greenish, do not wait for yellowing.
Not a single person will refuse the fruits of the Williams variety, and therefore, despite some of the shortcomings of this variety, it is worth growing in their country houses and personal plots.
